Colombia designates estuary and mangrove site on the Pacific Coast for World Environment Day

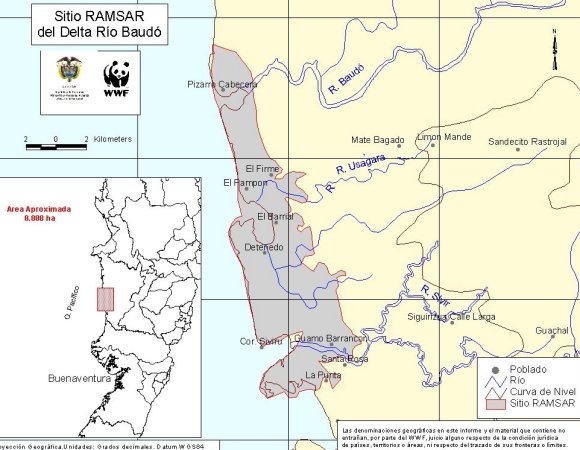
Colombia, whose Pacific coastline is a hotspot for biological diversity, designated the Baudó River Delta as the country's third Ramsar Site, a timely designation for World Environment Day, the focus of which this year is on the oceans. The site (8,888 ha, 04°50' N; 077° 20' W) is the estuary of the Baudó river, which like the rest in the Pacific basin of Colombia is relatively short but has a very high flow. The delta comprises flood banks, sand beaches, shrub-swamps and swamp forests. Outstanding vegetation includes the nato mangroves (Mora oleifera, Mora megistosperma), with trees reaching 35 m or more in height; mangrove forests (Pelliciera rhizophorae, Avicennia germinans), and giant reeds. Noteworthy fauna include the Spotted Paca (Agouti paca), the peccaries (Tayassu pecari and Tayassu tajacu), Jaguar (Panthera onca) and Neotropical Otter (Lontra longicaudis). The wetland is habitat and reproduction site of numerous species of fish such as the cichlid Cichlasoma kraussii, the Trahira (Hoplias malabaricus) and the Flathead mullet (Mugil cephalus). Uses of the site by human communities include forest exploitation, fishing, subsistence agriculture, hunting and basket-making. The highest concerns come from mangrove felling, overfishing, uncontrolled hunting, boat transportation with off-board engines and the clearing for rice cultivation. The Ramsar Site had no previous conservation category; nevertheless, its conservation  status is high. Surrounding areas are the collective property of black communities. The designation process was carried out by the Ministry of the Environment, Housing and Territorial Development and supported by WWF International's Living Waters Programme and WWF-Colombia, the Pizarro municipality, CODECHOCO, Asociación Calidris and the Instituto de Estudios Ambientales del Pacífico. Ramsar Site no. 1387.
status is high. Surrounding areas are the collective property of black communities. The designation process was carried out by the Ministry of the Environment, Housing and Territorial Development and supported by WWF International's Living Waters Programme and WWF-Colombia, the Pizarro municipality, CODECHOCO, Asociación Calidris and the Instituto de Estudios Ambientales del Pacífico. Ramsar Site no. 1387.